
Redis on Microsoft Azure Workload Brief
Dpsv5 Virtual Machines Powered by Ampere Altra Processors
Overview
Ampere® Altra® processors are designed to deliver exceptional performance for cloud native applications like Redis. They do so by using an innovative architectural design, operating at consistent frequencies, and using single-threaded cores that make applications more resistant to noisy neighbor issues. This allows workloads to run in a predictable manner with minimal variance under increasing loads. The processors are also designed to deliver exceptional energy efficiency. This translates to industry leading performance/watt capabilities and a smaller carbon footprint.
Microsoft offers a comprehensive line of Azure Virtual Machines featuring the Ampere Altra Cloud Native processor that can run a diverse and broad set of scale-out workloads such as web servers, open-source databases, in-memory applications, big data analytics, gaming, media, and more. The Dpsv5 VMs are general-purpose VMs that provide 4 GB of memory per vCPU and a combination of vCPUs, memory, and local storage to cost-effectively run workloads that do not require larger amounts of RAM per vCPU. The Epsv5 VMs are memory-optimized VMs that provide 8 GB of memory per vCPU, which can benefit memory-intensive workloads, including open-source databases, in-memory caching applications, gaming, and data analytics engines.
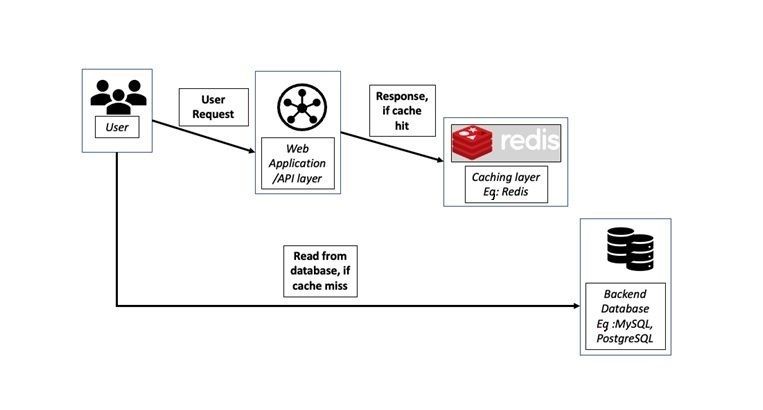
Redis is an open-source, in-memory, key-value data store that is typically used as a database or a cache. It uses an in-memory dataset, but data can be persisted through periodic writes or appends to disk. Due to its in-memory nature, Redis is extremely fast, and it can deliver high throughput at sub-millisecond latencies. It continues to rank highly in popularity among key value stores in the cloud, according to DB-engines.
Results and Key Findings
As can be seen in the chart above, we observed up to a 16% improvement in performance on the Microsoft Azure Dpsv5 VMs powered by Ampere Altra processors compared to the Intel Icelake VMs, and 9% better than the AMD Milan ones, all under an p99 SLA of 1ms.
In addition, the Azure Dpsv5 VMs also offer compelling price-performance compared to similar legacy x86 VMs. A 16vCPU Ampere Altra VM offered up to 45% better price-performance than the x86VMs.
Benchmarking Configuration
We have used memtier_benchmark (developed by Redis Labs) as a load generator for benchmarking Redis. Each test was configured to run with multiple threads, multiple clients per thread, and with pipelining enabled.
We recommend compiling Redis server with GCC (GNU Compiler Collection) 10.2 or newer as recent compilers have made significant progress towards generating optimized code for AArch64 applications.
We used Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.1 (5.14.0-162.6.1.el9_1) with Redis-server 6.0.12 for our tests. For each of the tests, we used similar clients to generate requests to Redis-server.
Since it is realistic to measure throughput under a specified Service Level Agreement (SLA), we have used a 99th percentile latency (p.99) of 1 ms. This ensures that 99% of the requests have a response time of 1ms in the worst case.
The test ran for 3 minutes with a 1:10 get:set ratio, which is common for in-memory caches. We initially used an appropriate number of clients and threads/client to load one instance of Redis, while ensuring the p.99 latency was at most 1 ms. Pipelining is a feature whereby Redis can process new requests even when the client has not already read older responses. This feature can dramatically reduce response times.
Next, we successively increased the number of Redis instances till one or more instances violated the p.99 latency SLA. The aggregate throughput of all instances was used as the primary performance metric. We ran the test three times and saw minimal run-to-run variations.
Key Findings and Conclusions
Fast in-memory caches are used in most cloud usages today. Redis is a popular high throughput in-memory key-value store that is applicable to low latency applications in a scale-out configuration. For cloud application developers, choosing Ampere Altra-based VMs on Azure means better performance and price-performance while reducing your carbon footprint
For more information about Azure Virtual Machines with Ampere Altra Arm-based processors, visit the Azure blog.
Footnotes
All data and information contained herein is for informational purposes only and Ampere reserves the right to change it without notice. This document may contain technical inaccuracies, omissions and typographical errors, and Ampere is under no obligation to update or correct this information. Ampere makes no representations or warranties of any kind, including but not limited to express or implied guarantees of noninfringement, merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose, and assumes no liability of any kind. All information is provided “AS IS.” This document is not an offer or a binding commitment by Ampere. Use of the products contemplated herein requires the subsequent negotiation and execution of a definitive agreement or is subject to Ampere’s Terms and Conditions for the Sale of Goods.
System configurations, components, software versions, and testing environments that differ from those used in Ampere’s tests may result in different measurements than those obtained by Ampere.
Price performance was calculated using Microsoft's Virtual Machines Pricing, in September of 2022. Refer to individual tests for more information.
©2022 Ampere Computing. All Rights Reserved. Ampere, Ampere Computing, Altra and the ‘A’ logo are all registered trademarks or trademarks of Ampere Computing. Arm is a registered trademark of Arm Limited (or its subsidiaries). All other product names used in this publication are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of their respective companies.
Ampere Computing® / 4655 Great America Parkway, Suite 601 / Santa Clara, CA 95054 / amperecomputing.com
