NGINX on Azure VMs based on Ampere
Performance
NGINX is a high-performance HTTP web server that is widely used for cloud web applications. As a web server, the performance of NGINX depends on compute, memory, and network performance. This makes it a great test subject for the overall performance of our processors.
While benchmark testing in our labs, we configured NGINX to serve a static HTML file over HTTPS. The workload generator was configured to run under increasing load from multiple clients, with a strict SLA. In our tests, we found that NGINX performance on Ampere Altra Max was up to 3.2 times faster than equivalent Intel Xeon Icelake 8380 and 1.83 times faster than AMD EPYC Milan 7763 at a socket level.
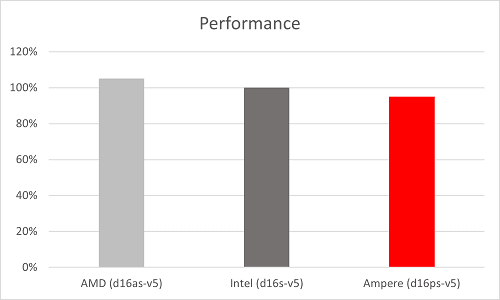
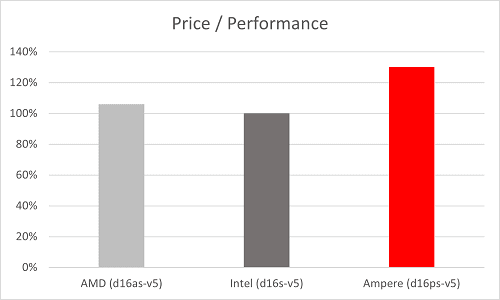
We also tested NGINX on Ampere Altra instances on Azure, comparing Ampere Altra Dpsv5 instances with comparable x86 instances. We found that Ampere Altra instances are at least 30% better in price-performance compared to Intel instances and 22% compared to AMD instances.
In the past decade, we have seen the power consumption of cloud service providers explode, with Bloomberg estimating in 2020 that cloud computing consumed 1% of the world’s electricity and predicting that this would rise to 8% of the world’s energy consumption by the end of the decade.
Ampere microprocessors provide best-in-industry power efficiency per core, allowing cloud service providers to scale the compute resources they provide to customers, without increasing their energy consumption.
In our testing of NGINX, we found that Ampere Altra Max processors used up to 73% less power at comparable performance to x86 platforms. Up to 69% fewer Ampere Altra Max processors were required to deliver 1 million requests per second. For cloud application developers, choosing Ampere instances means reducing the amount of compute resources, and reducing the total power required to deliver similar performance. You can reduce the carbon footprint of your cloud applications, while maintaining high performance at a much lower cost.
Performance data on Azure Public Preview as of 7/1/2022.
